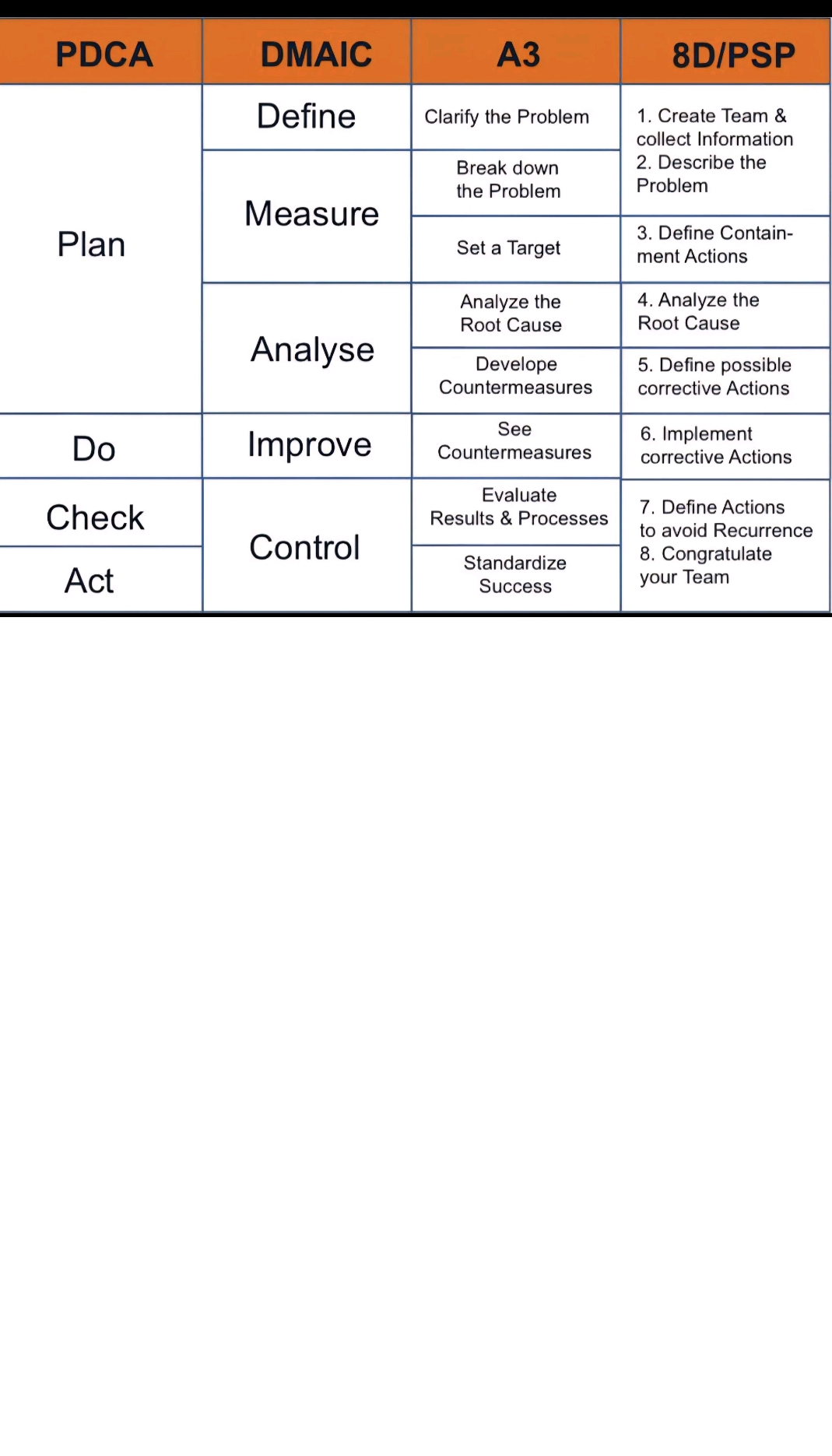
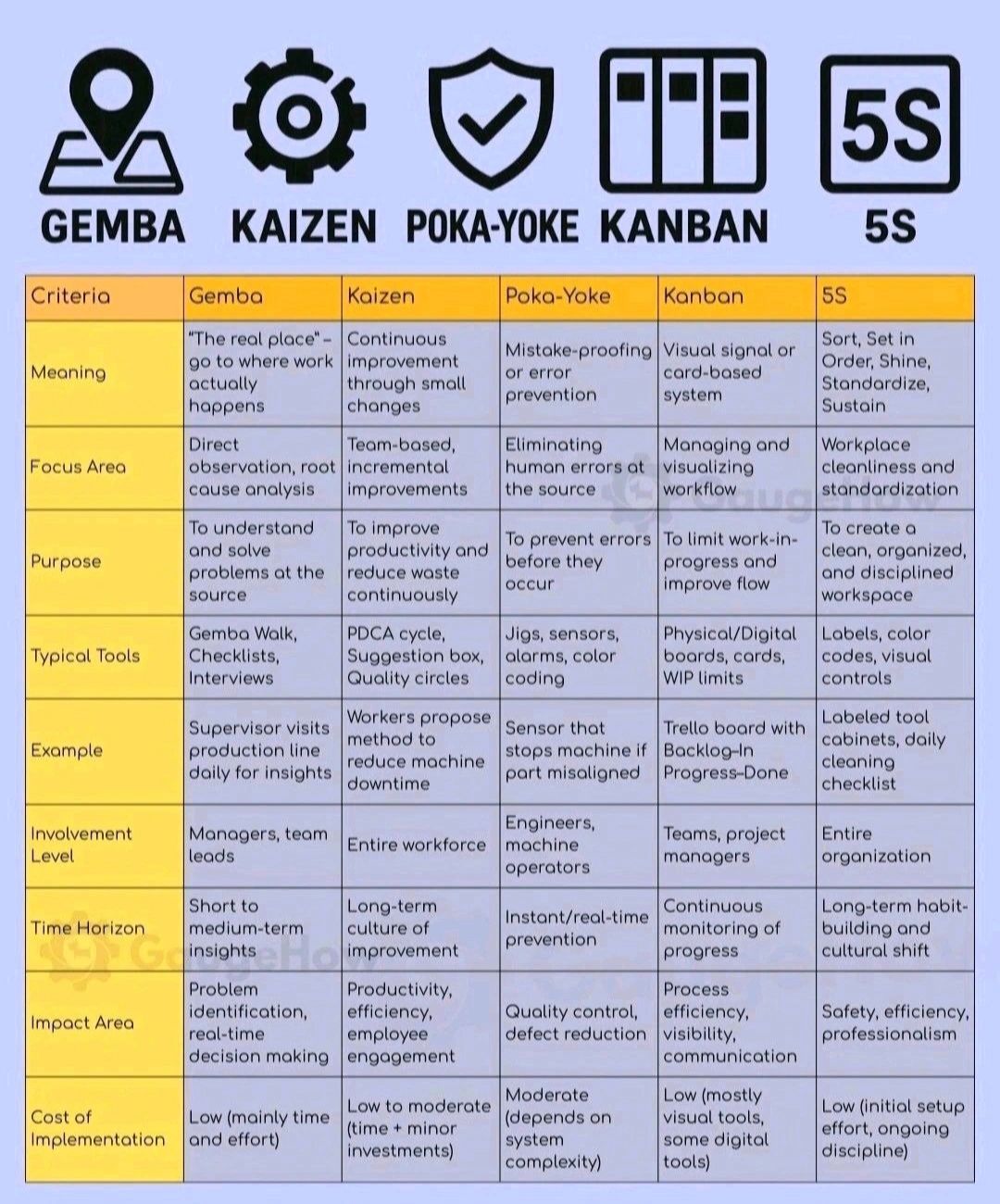
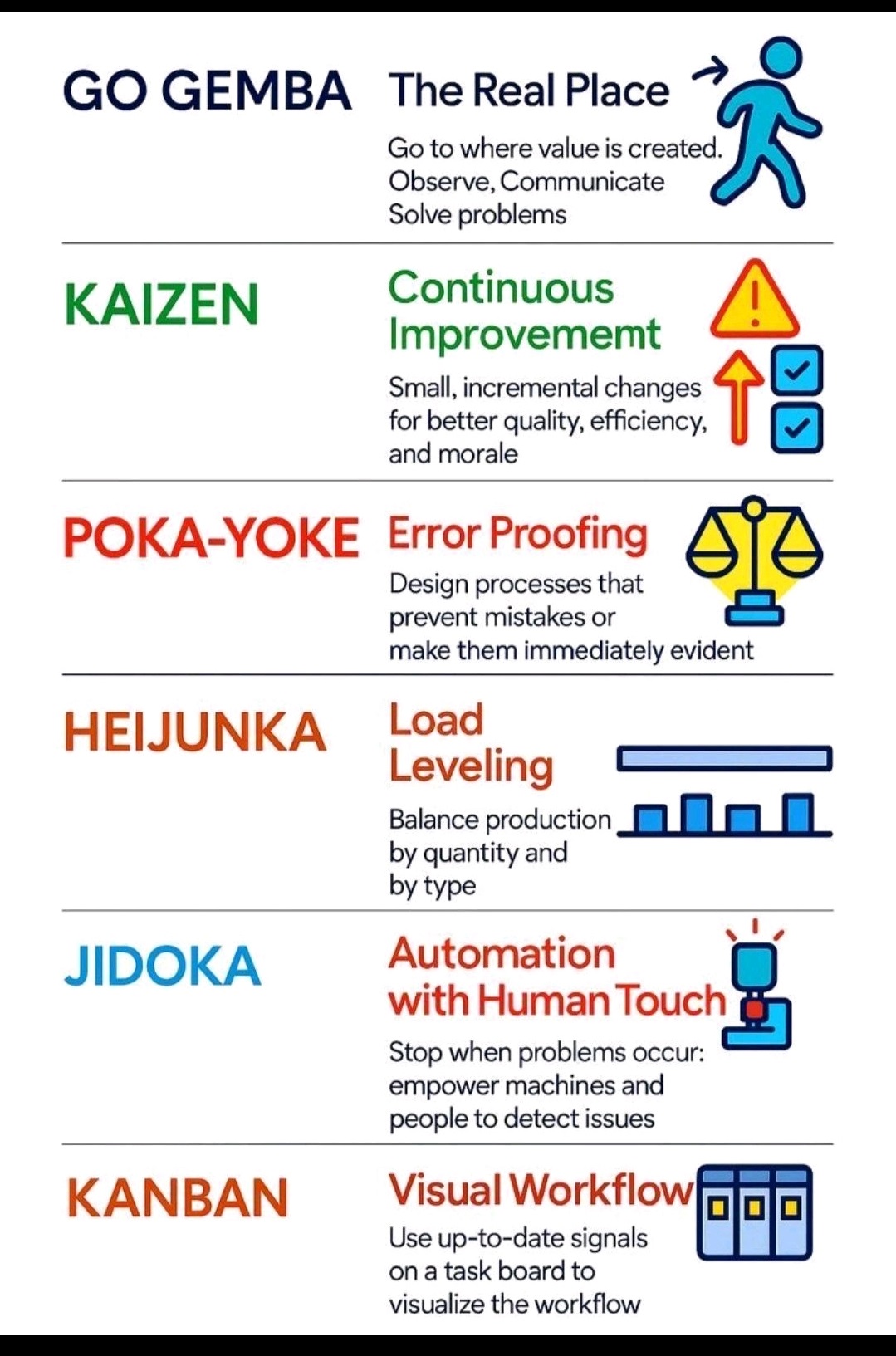
Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing)


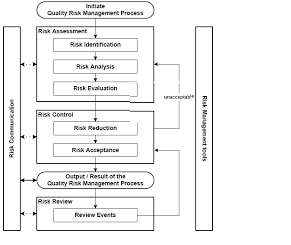
Quality Risk Management (QRM) is a systematic, science-based approach to identifying, assessing, controlling, communicating, and reviewing risks to product quality throughout its lifecycle. The goal is to ensure product safety and quality.
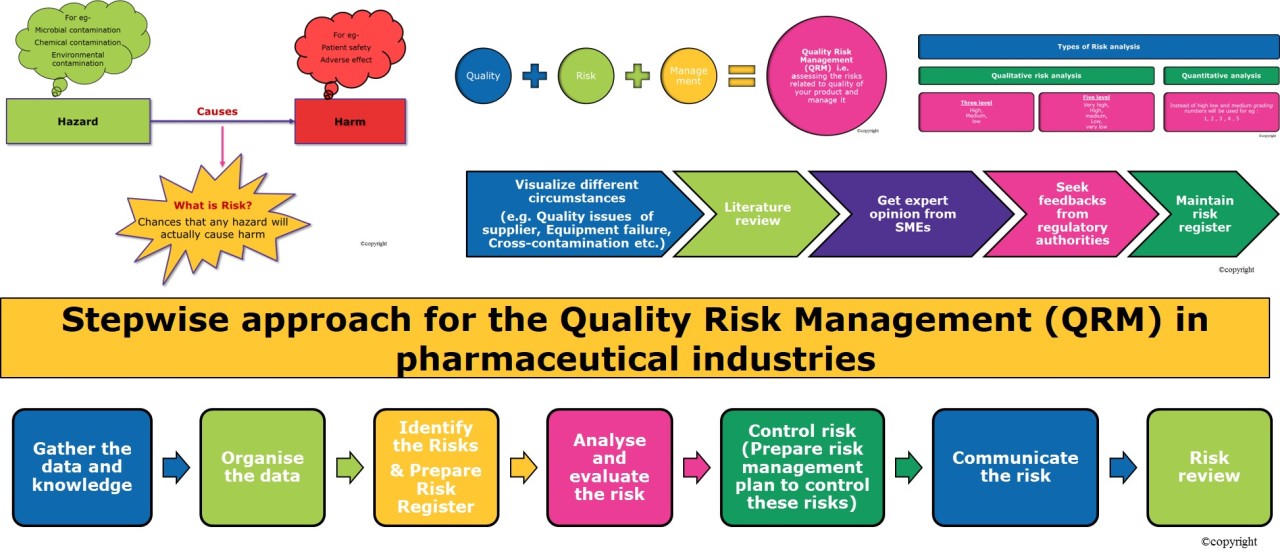
Key components of the QRM process
Benefits of Quality Risk Management

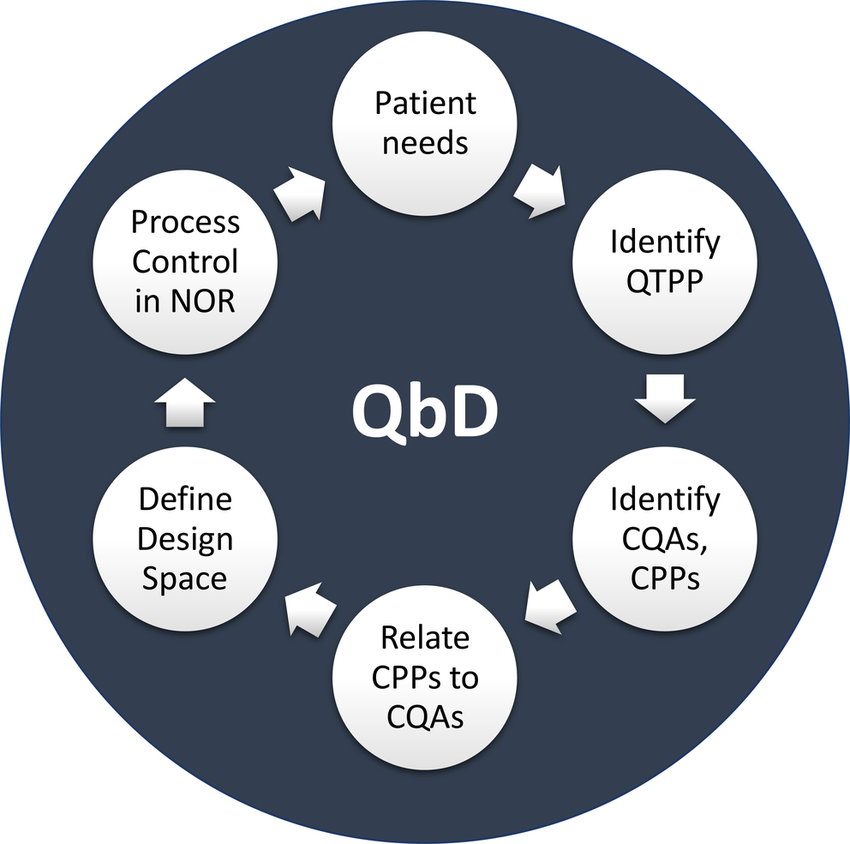
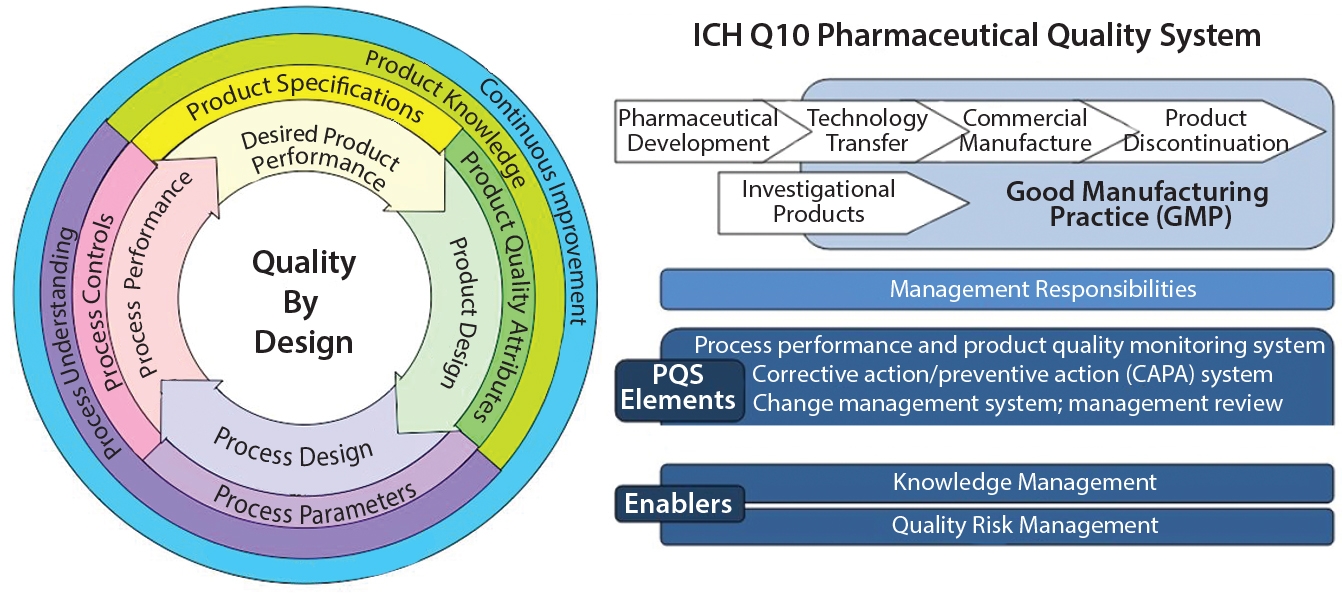
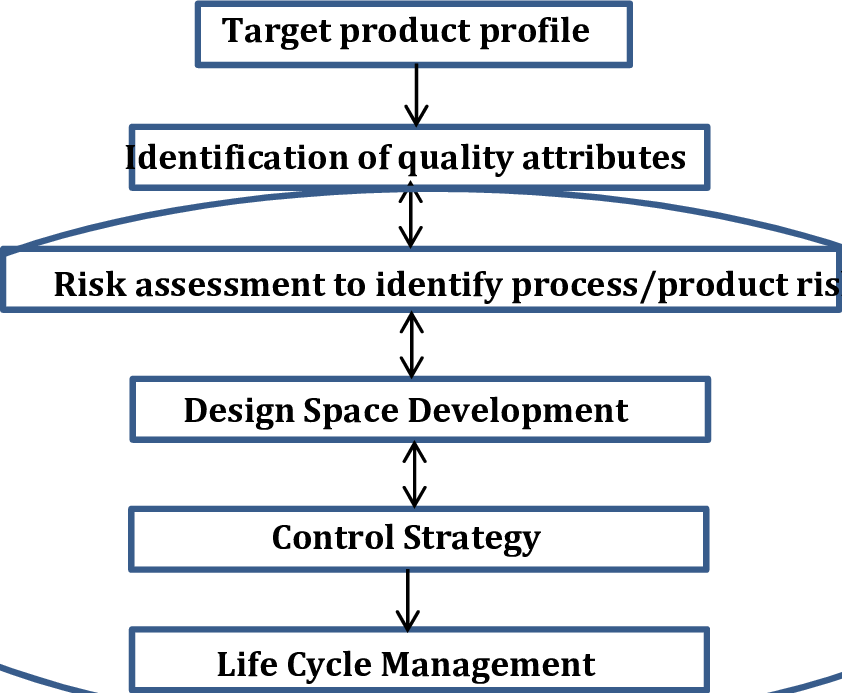
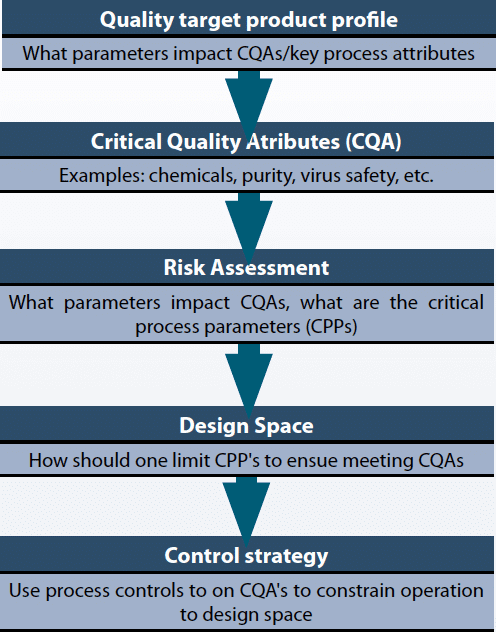
Quality by Design (QbD) is a systematic approach to product development that builds quality in from the start by focusing on a deep understanding of the product and its manufacturing process. It uses a science-based, risk-management approach to identify critical quality attributes (CQAs) and critical process parameters (CPPs), establishing a “design space” and control strategy to consistently meet quality targets throughout the product lifecycle.
Key principles and steps :-

Regulatory Definitions of Data Integrity
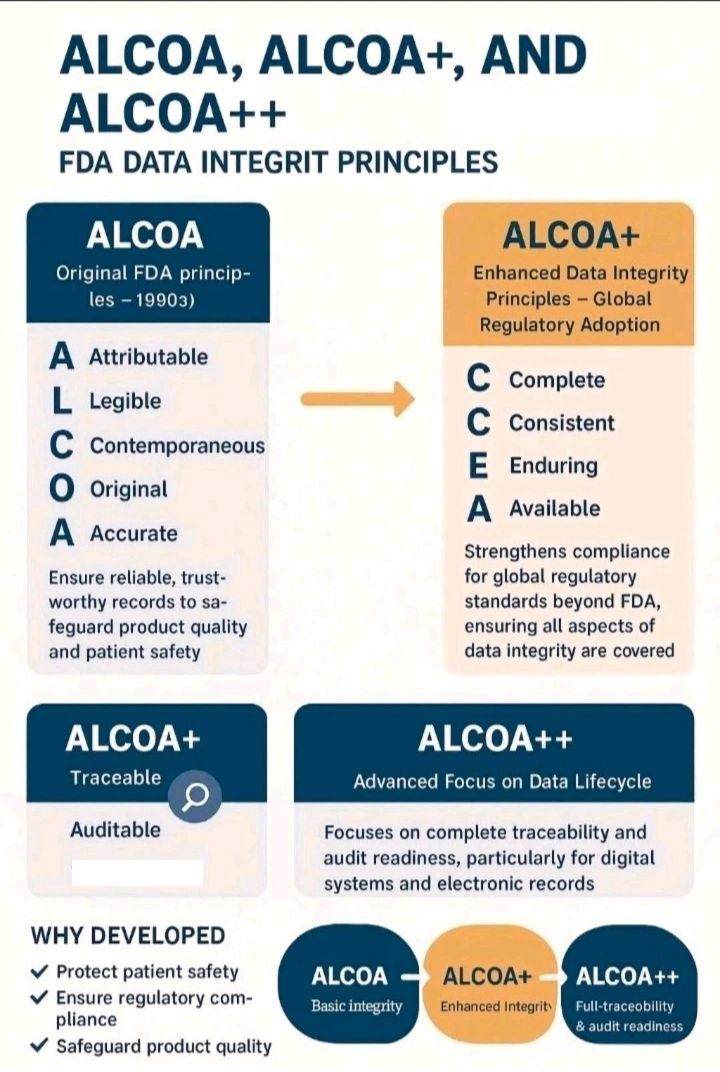
USFDA: “Data integrity refers to the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data. Complete, consistent, and accurate data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded original, and accurate (ALCOA)”.
MHRA: “The extent to which all data are complete, consistent, and accurate throughout the data lifecycle.”
WHO: “Data integrity is the degree to which a collection of data is complete, consistent and accurate throughout the data lifecycle. The collected data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original or a true copy, and accurate”.
PICS: “Data Integrity is defined as the extent to which all data are complete, consistent, and accurate, throughout the data lifecycle”.

Regulatory Definitions of Data Integrity
USFDA: “Data integrity refers to the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data. Complete, consistent, and accurate data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded original, and accurate (ALCOA)”.
MHRA: “The extent to which all data are complete, consistent, and accurate throughout the data lifecycle.”
WHO: “Data integrity is the degree to which a collection of data is complete, consistent and accurate throughout the data lifecycle. The collected data should be attributable, legible, contemporaneously recorded, original or a true copy, and accurate”.
PICS: “Data Integrity is defined as the extent to which all data are complete, consistent, and accurate, throughout the data lifecycle”.
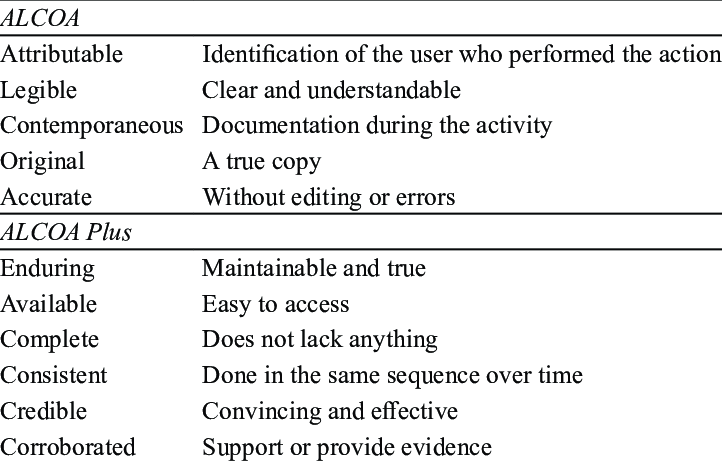
| Attributable | The Identity of the person completing a record (Who, When, Why). |
| Legible | The data is readable, Understandable, Traceable, Permanent allowing for a clear picture of the activities that occurred. |
| Contemporaneous | The data is recorded at the time it is generated or observed (No Back dating). |
| Original | Original Records must preserve data accuracy, completeness, content and meaning. Data as the file or format in which it was initially generated. |
| Accurate | The data record must be accurate whether paper or electronic, it must be exact, true and free from error (this might require a second verification if necessary). |
| Consistent | Consistent application of date and time stamps in the expected sequence. |
| Complete | All Information needs to be maintained. Batch pass-fail, Reanalyses carried out. (OOS, OOT). |
| Enduring | Medium used to record data should be permanent and not temporary memory RAM. |
| Available | Available/Accessible for review / audit for the life time of the record. |