Skip to the content
TOPIC- DISSOLUTION
Definition:
Dissolution is a process in which a solid substance solubilizes in a given solvent i.e. mass transfer from the solid surface to the liquid phase.
Dissolution is the rate determining step for hydrophobic,
poorly aqueous soluble drugs.
Why dissolution studies?
-
To show that the release of drug from the tablet is close to 100%.
-
To show that the rate of drug release is uniform batch to batch.
-
And to show that release is equivalent to those batches proven to be bioavailable and clinically effective.
Apparatus Classification in USP:
-
Apparatus 1 (rotating basket)
-
Apparatus 2 (paddle assembly)
-
Apparatus 3 (reciprocating cylinder)
-
Apparatus 4 (flow-through cell)
-
Apparatus 5 (paddle over disk)
-
Apparatus 6 (cylinder)
-
Apparatus 7 (reciprocating holder)
A drug product is considered rapidly dissolving when;
no less than 85% of the labeled amount of the drug substance dissolves within 30 minutes, using USP Apparatus I at 100 rpm (or Apparatus II at 50 rpm) in a volume of 900 ml or less in each of the following media:
-
1 N HCl or Simulated Gastric Fluid USP without enzymes;
-
a pH 5 buffer; and
-
a pH 8 buffer.
Biopharmaceutical Classification System;
Class I:
High solubility—High permeability
Class II:
Low solubility—High permeability
Class III:
High solubility—Low permeability
Class IV:
Low solubility—Low permeability
Why Qualification & Validation of the Apparatus?
-To maintain “quality by design”.
-Physical & chemical calibrations—for geometrical & dimensional accuracy & precision.
-Vibration or undesired agitation to be avoided.
-Temperature, rotation speed/flow rate, volume, sampling probe, procedures, etc. need to be monitored periodically.
Use of USP calibrator tablets for App. 1 & 2 (to be performed not less than twice a year)
Solubility of solid in dissolution medium;
-
Temperature of dissolution medium.
-
pH of the medium.
-
Solubility of the drug in dissolution medium.
-
Presence of co-solvents.
Dissolution rate constant
Depend upon;
-
Thickness of boundary layer
-
Degree of agitation
-
Speed of stirring
-
Shape, size & position of stirrer
-
volume of dissolution medium
-
Shape & size of container
-
Viscosity of dissolution medium
-
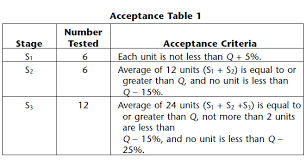
Dissolution Acceptance Criteria in case of Failure;
THANK YOU
error: Content is protected !!

