TOPIC :- HUMAN ERRORS
Understanding Human Errors.
Investigation of human errors.
Regulatory expectations.
CAPAs.
Current way of handling human errors.
Case study.
Human Error Is The Leading Cause Of GMP Deviations
25-60% of the deviations / Incidents in the companies are caused by Human errors
Human Errors-Regulatory Observations :-
Warning Letter / FDA 483
- Foreign matter was identified as a known process-related defect, yet no specific root cause for the particulate was identified. And the most likely root cause of failure to identify the critical/major defects during 100% visual inspection was identified as human error.
- High percentage rate of invalidated OOS (77%)test results without appropriate investigation was identified contributing mainly because of human error, instrument/column error, and method error.
- Multiple LI investigations lacked scientific rationale for root cause Probable root cause were attributed to contamination and analyst error
- CAPAs have often been limited to retraining Improvement in analytical methods and equipment were not generally implemented to enhance robustness and prevent error.
Current CAPAs
- Training / Re-training
- Display notification
- Take actions on the employee
- One point lesson
- Revise SOP
Human Error Classification Table
| Action Type | Subtype | Description | Error Type | Associated Gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unintended Action | Slip of Action | Error in execution (e.g., pressing wrong key) | Execution Error | Attention Gap |
| Lapse of Memory | Forgetting a step or detail | Memory Error | Attention Gap | |
| Rule-Based Mistake | Misapplying a known rule or SOP | Decision/Rule Error | Understanding Gap | |
| Knowledge-Based Mistake | Inadequate knowledge or misjudgment | Knowledge/Skill Error | Proficiency Gap | |
| Intended Action | Situational Behavior | Action taken under pressure or poor judgment | Situational Deviation | Behavioral Gap |
| Exceptional Behavior | Deliberate rule-breaking or non-compliance | Intentional Deviation | Behavioral Gap |
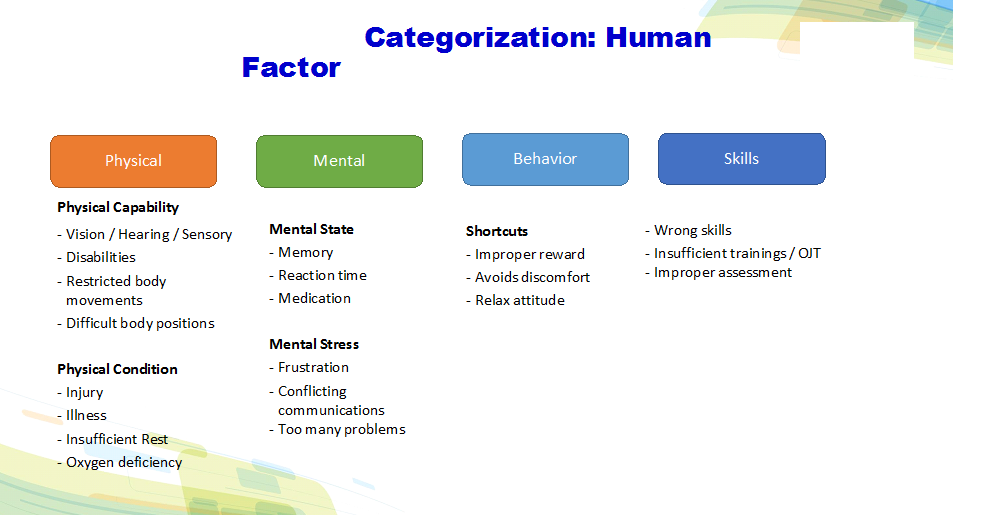

Important points for human error investigations
- Pre-defined Interview
- Photographic evidence
- Approved hypothesis plan (Wherever required)
- Spot verification (Gemba walks)
- Data analysis based on system, person, area, process, system etc
Summary
- Human errors do happen
- Categorize it as Human error after all possible causes have been
- Small quantity of deviations to result from human error
- Investigation should be thorough to ensure that cause is
- Eliminated any possible process, environment, procedural or system based issues.
- Classify human errors in Attention gap, understanding gap, skill gap and behavioral gap.
- Take appropriate actions based on the causes
- Look for error proofing instead of blame, duplication etc.
