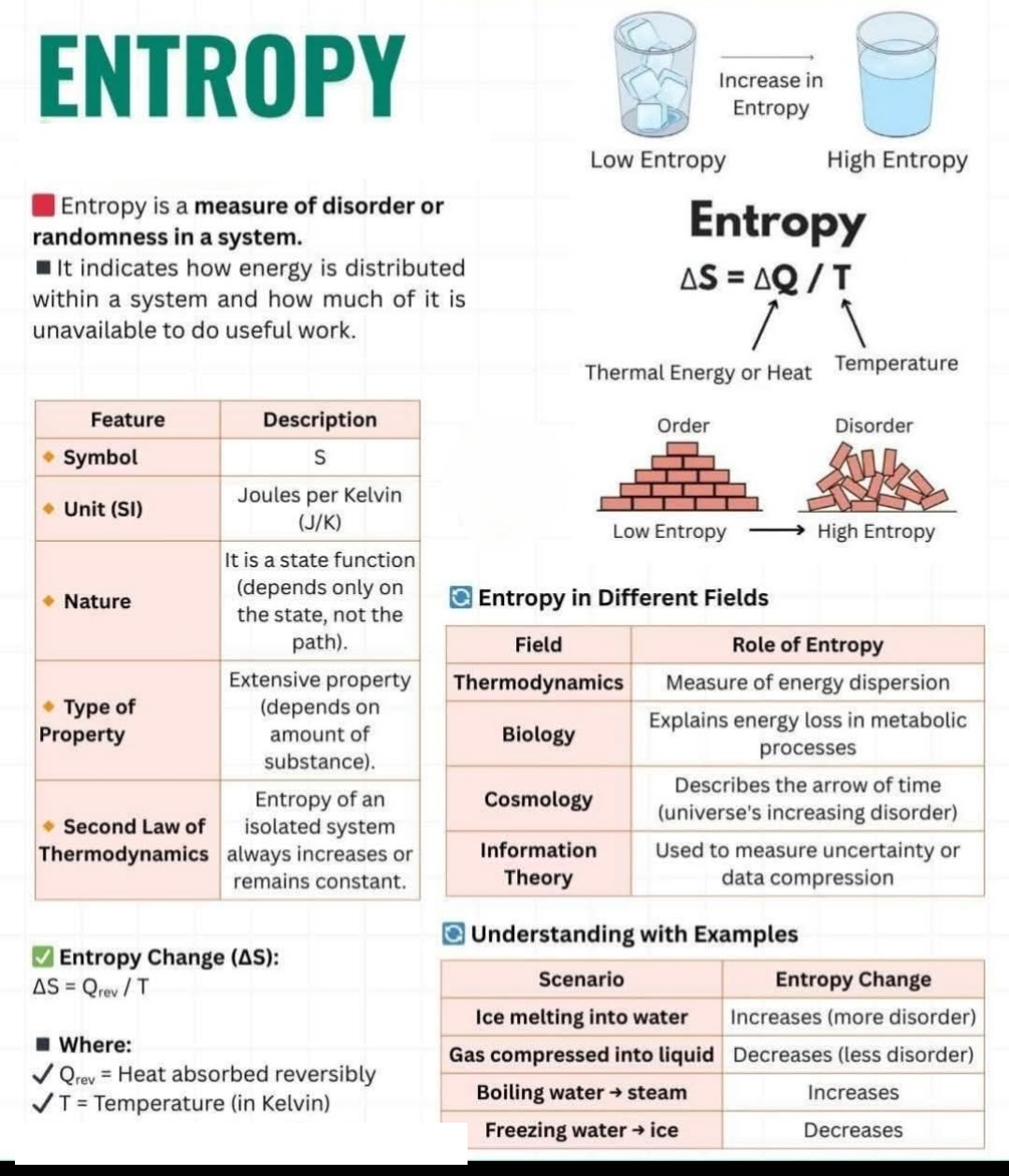
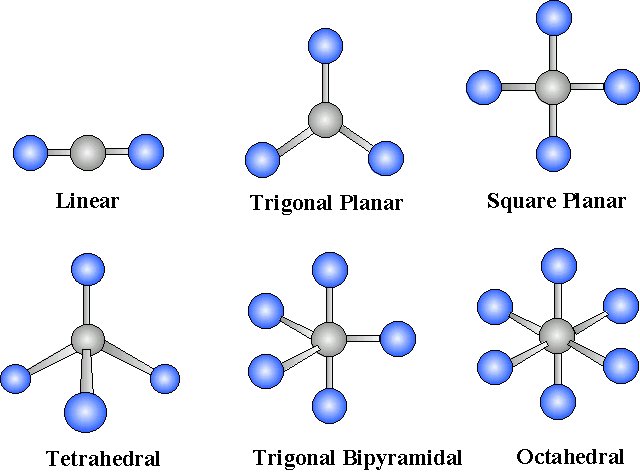
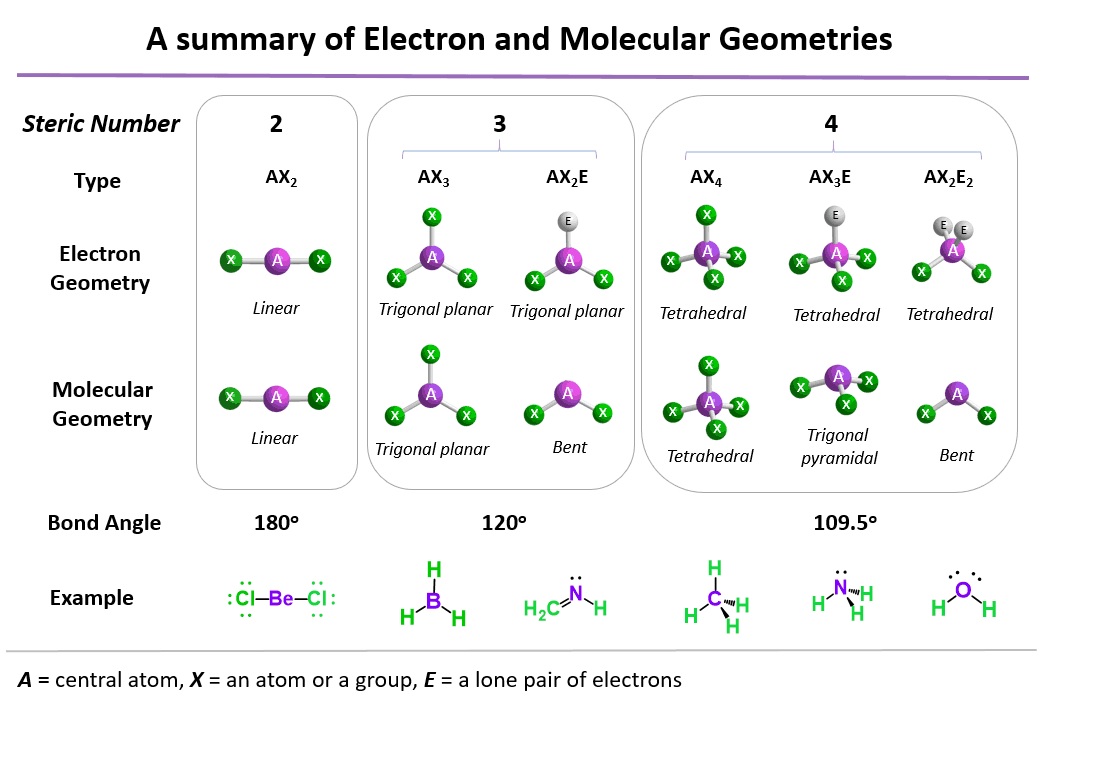
4.Complexometric Titration:
24.
What is Density?
Density is the measure of mass per unit volume.
Density = Mass/ Volume
25. What is Specific Gravity/ Relative Density?
The ratio of a substance’s density to the density of a reference substance (Water).
26. What is Weight per milliliter (wt/ml)?
Weight per milliliter (wt/ml) is a measure of density with units like grams per milliliter (𝑔/𝑚𝑙). Wt/ml tells absolute weight of particular volume.
27. What is Oxidation?
The loss of electrons or addition of Oxygen in substance.
e.g. C + O2 → CO2 (oxidation of carbon)
28. What is Reduction?
The gain of electrons or addition of Hydrogen in substance.
e.g. N2 + 3 H2 → 2NH3 ( reduction of nitrogen).
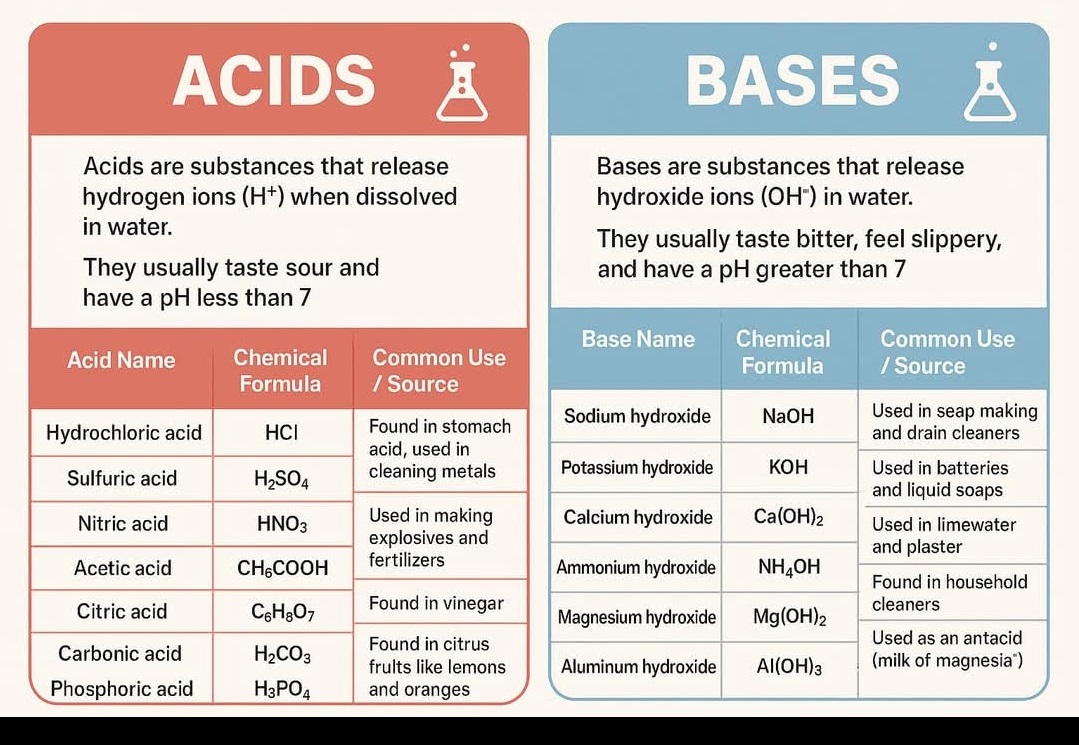
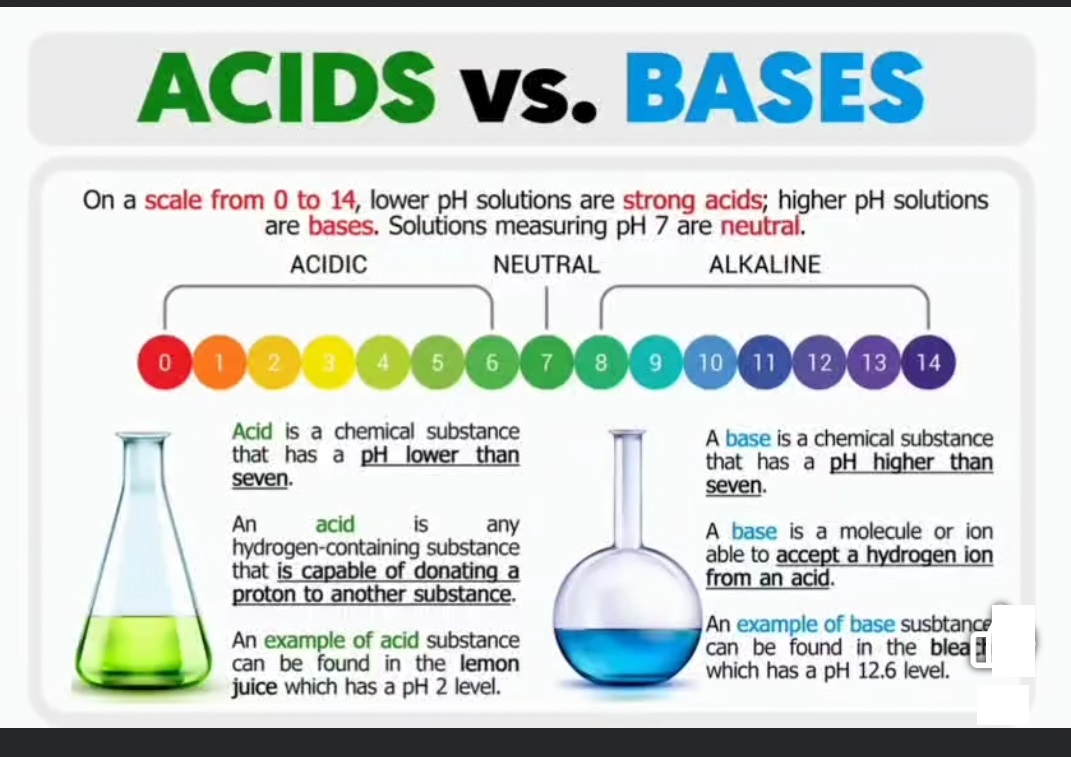
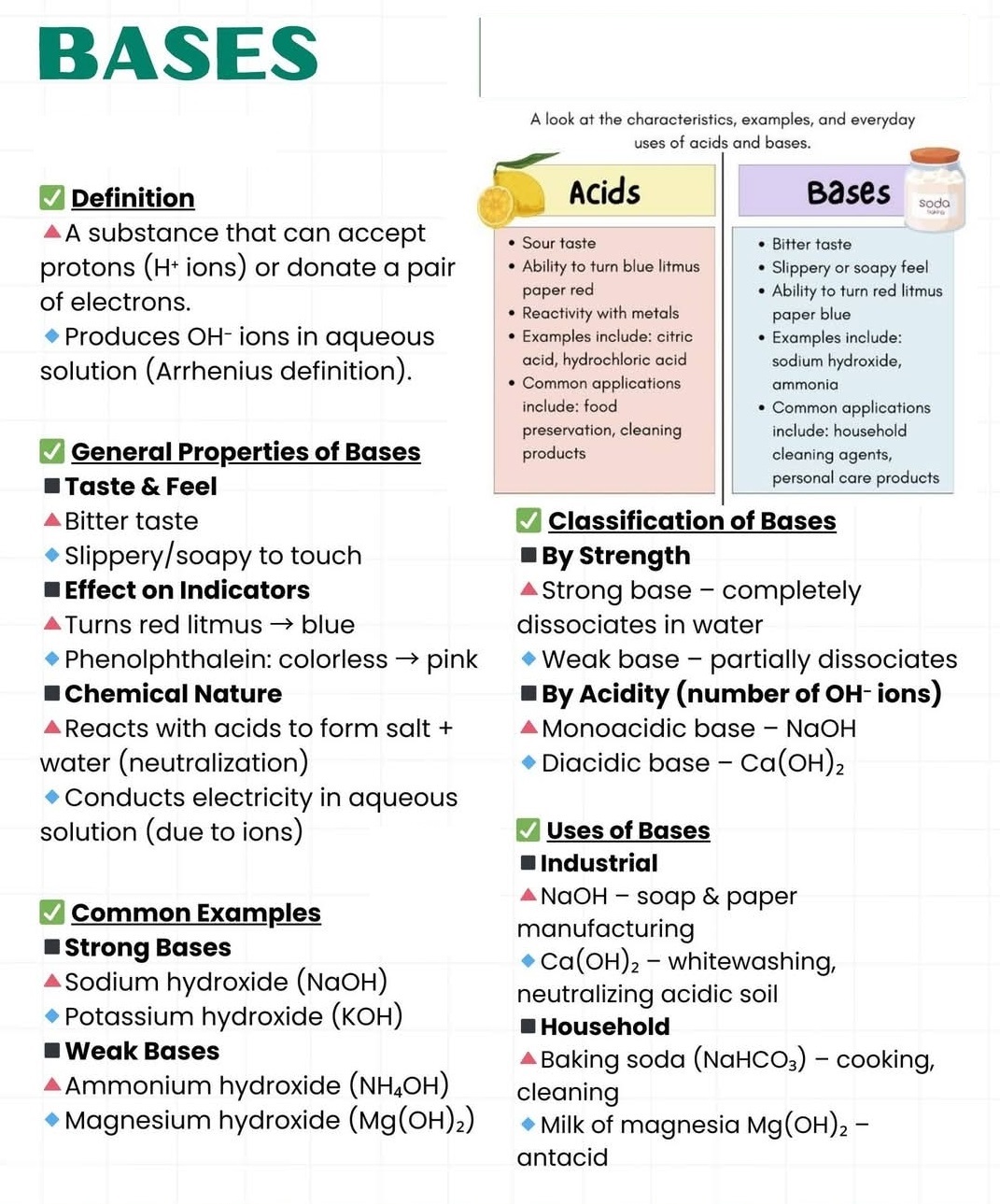
29. What are mineral Acids?
Sulfuric acid (𝐻2𝑆𝑂4), Hydrochloric acid (𝐻𝐶𝑙), and Nitric acid (𝐻𝑁𝑂3).
30. What is difference Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds?
Organic compounds always have a carbon atom, while most of the Inorganic compounds do not contain a carbon atom in them. Almost all organic compounds contain carbon-hydrogen or a simple C-H bond in them.
31. What is difference between Molecular weight and Equivalent Weight?
Molecular weight is the mass of one mole of a substance, a fixed value for a given compound.
Equivalent weight, is a variable value that depends on the substance’s role in a specific chemical reaction, calculated by dividing the molecular weight by its “n-factor” or valence. The n-factor represents the number of reactive units, such as protons or electrons, that a molecule can donate or accept.
32. What is the principle of UV Spectroscopy?
The Beer-Lambert law is the principle behind UV-Vis spectroscopy, which explains that light absorbance is directly proportional to both concentration (𝑐) and path length (𝑙).
33. What UV & Visible Range?
Ultraviolet (UV) region from 190 to 400 nm and the visible light region from 400 to 800 nm.
34. What is Monochromatic light?
Light with a single wavelength or frequency.
35. What is TLC Plate?
It is combination of the plate’s stationary phase, support material, and any additional features like a fluorescent indicator. Common stationary phases include silica gel and alumina, while common support materials are glass, aluminum, or plastic.
36. What is Principle of IR?
The principle of Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is that molecules absorb infrared radiation at specific frequencies that match the vibrational frequencies of their chemical bonds, such as stretching or bending.
37. What is IR Range?
The full IR spectroscopy range is typically 12,800–10 cm⁻¹
Mid IR-4,000–400 cm⁻¹
38. What is the principle of Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS)?
The process involves atomizing the sample, exposing it to light of a specific wavelength from a hollow cathode lamp, and then measuring how much light is absorbed by the sample’s atoms as they make the transition from the ground state to an excited state.
39. What is the principle of Mass spectroscopy?
Mass spectrometry principle is to ionize a sample, separate the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio (𝑚/𝑧), and then detect them to determine their relative abundance.
40. What is Gas chromatography (GC)?
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common analytical technique used to separate, identify, and quantify volatile compounds in a mixture. It works by passing a mobile gas phase through a stationary phase (a column), which separates compounds based on their boiling points, polarity, and adsorption properties.
41. What is the difference between Polar and Non-Polar Molecules?
Polar molecules have an unequal sharing of electrons, creating partial positive and negative ends, while nonpolar molecules have an equal sharing, resulting in no distinct poles.
42. What is Gravimetric analysis ?
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative chemical technique that determines the amount of a substance by measuring its mass.
The four types of gravimetric analysis are precipitation, volatilization, electrogravimetry, and thermogravimetry.
44. What is the principle of colorimetry?
The absorbance of light by a colored solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing substance and the path length of the light through the solution.
45. What is Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)?
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is a technique that measures the weight change of a material as a function of temperature or time.
It is used to study a material’s properties, such as its thermal stability, composition, purity, decomposition reactions, and absorbed moisture content, by heating a sample in a controlled atmosphere.
46.