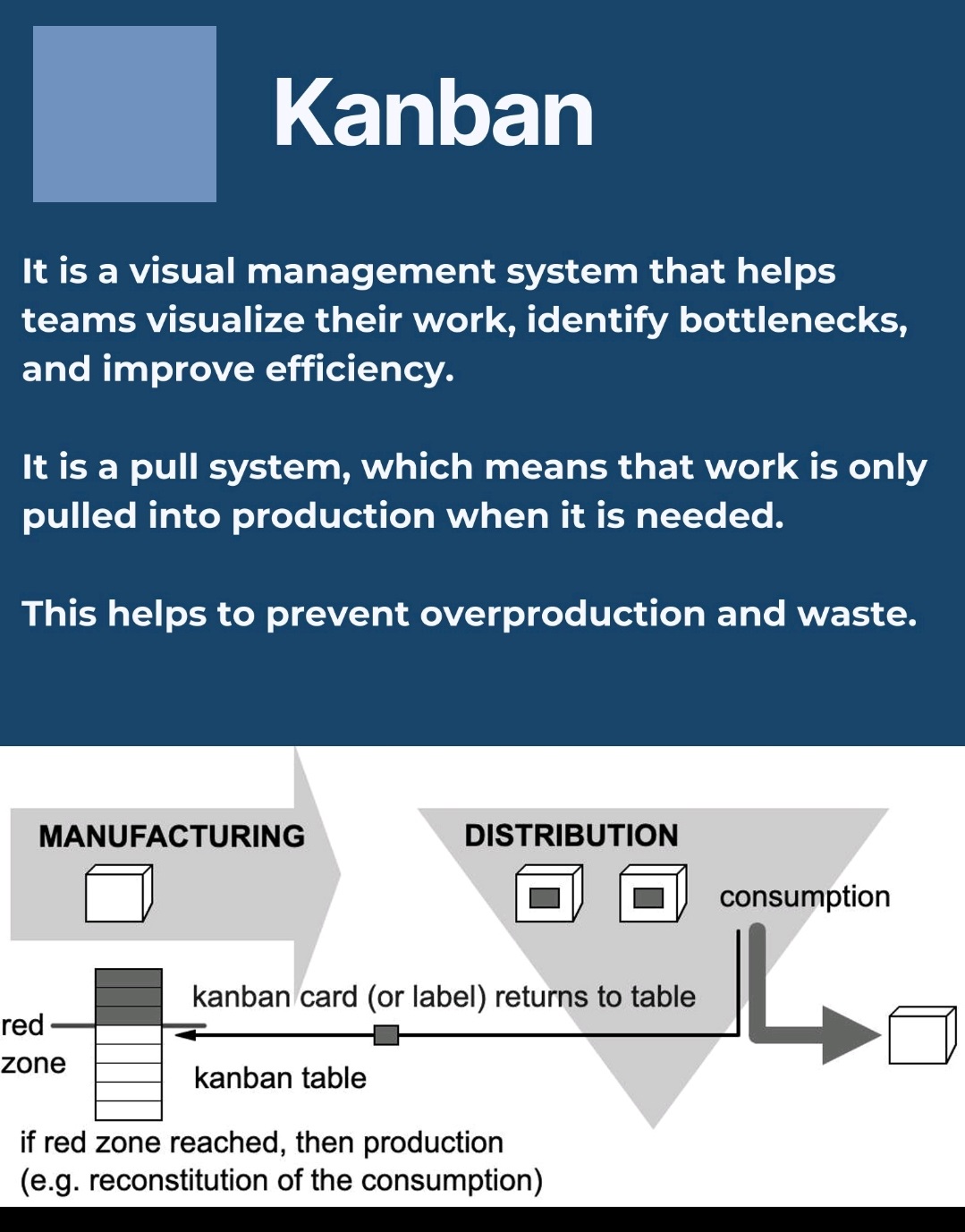
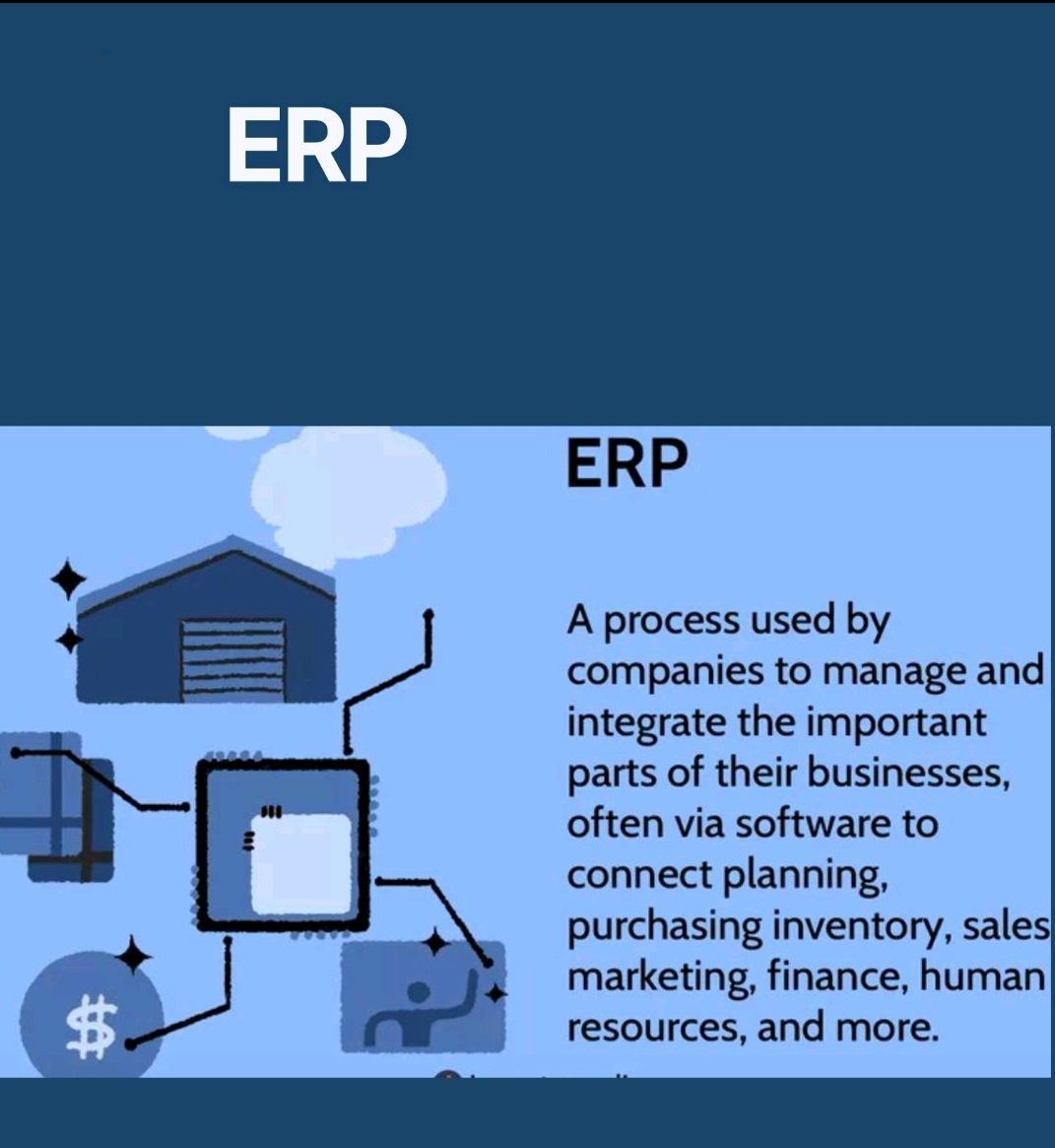
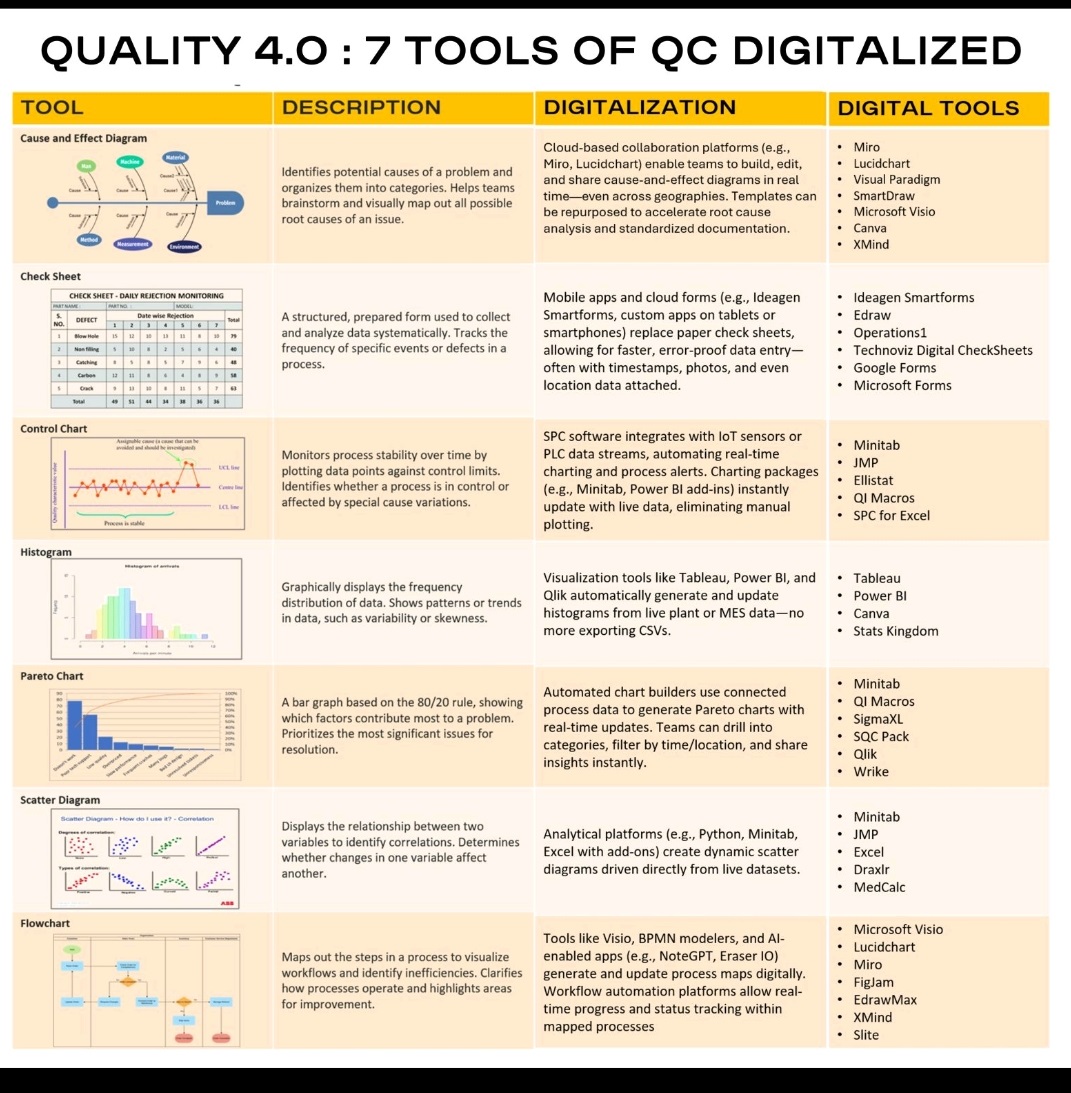
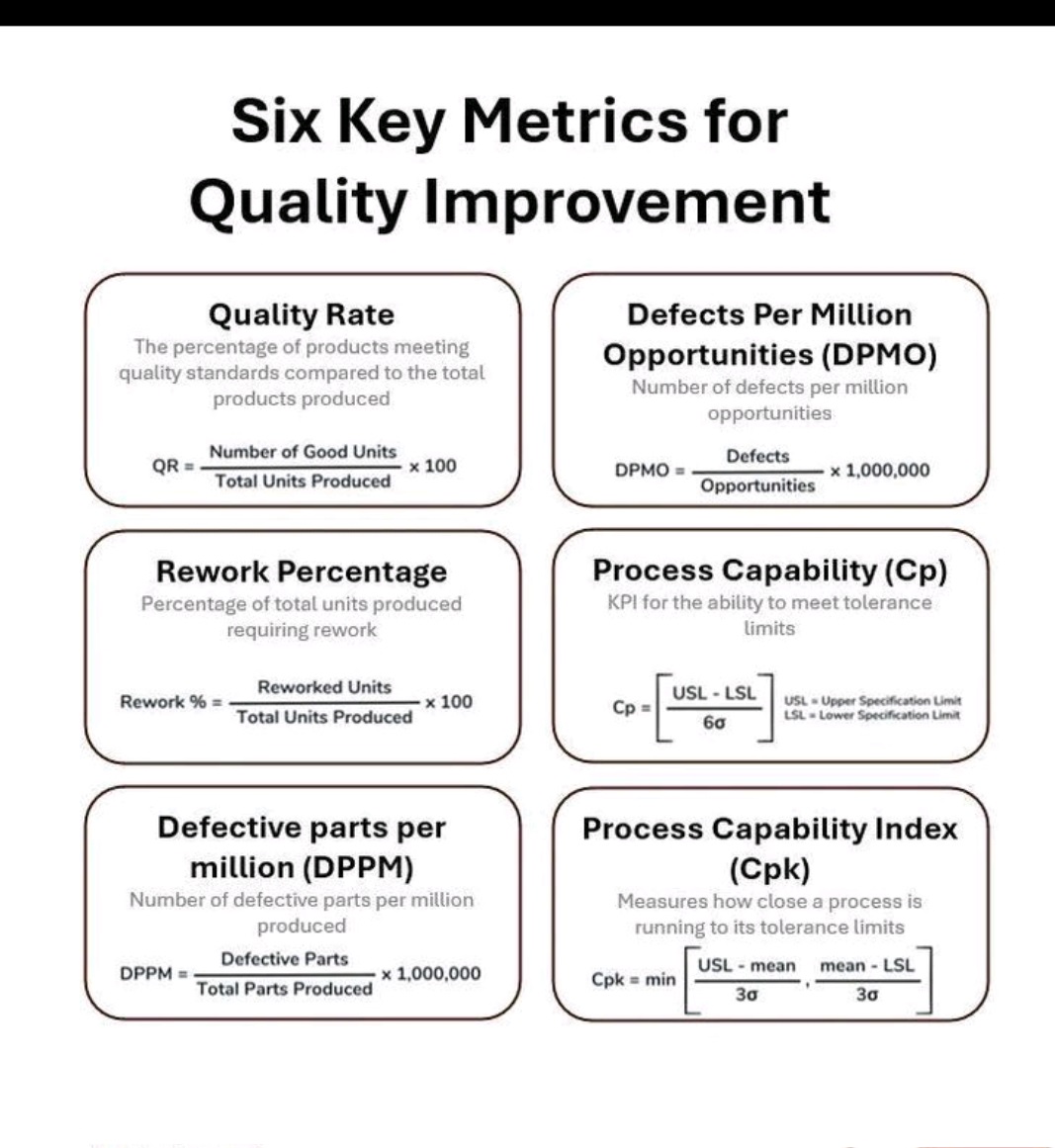
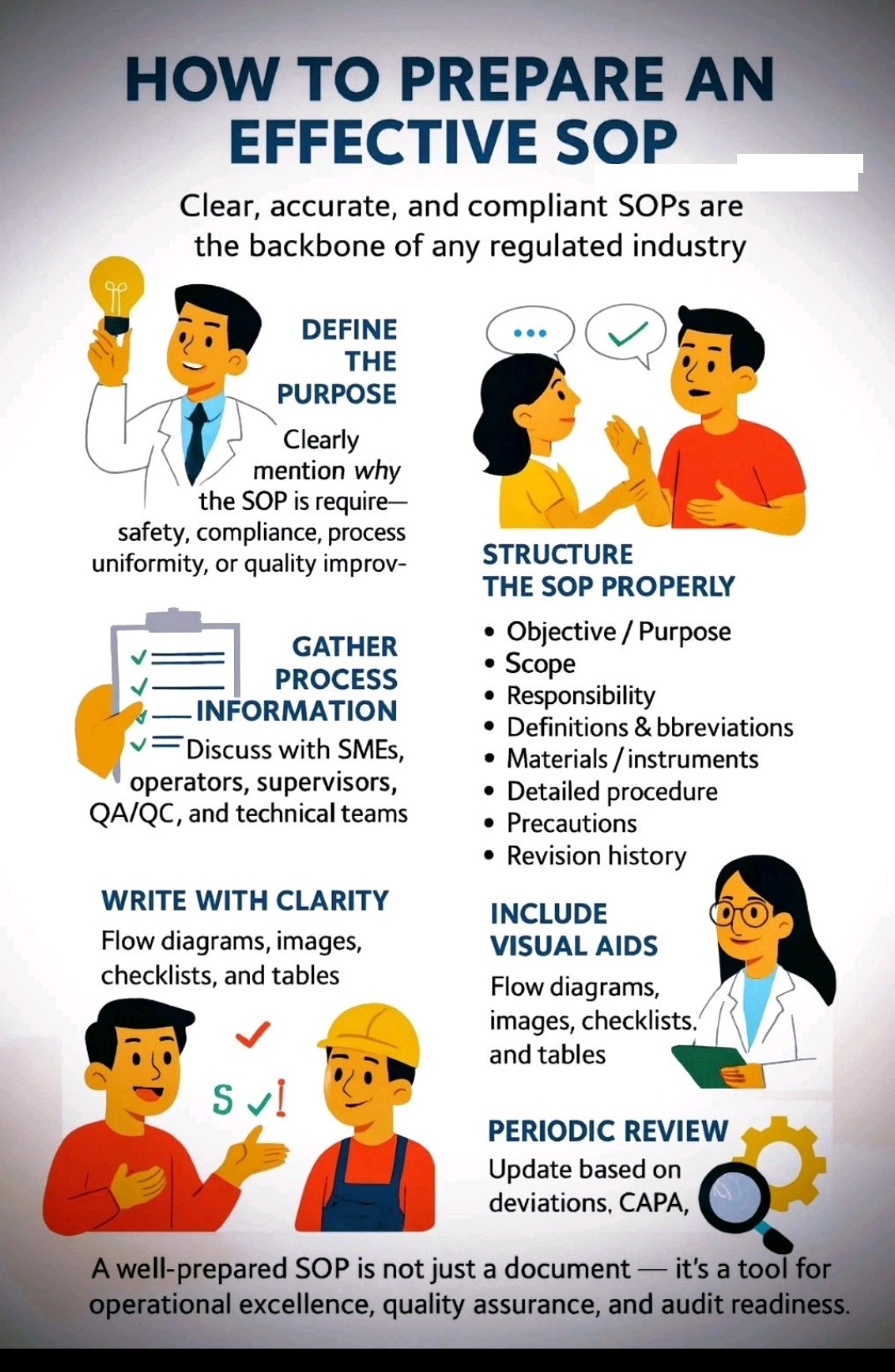
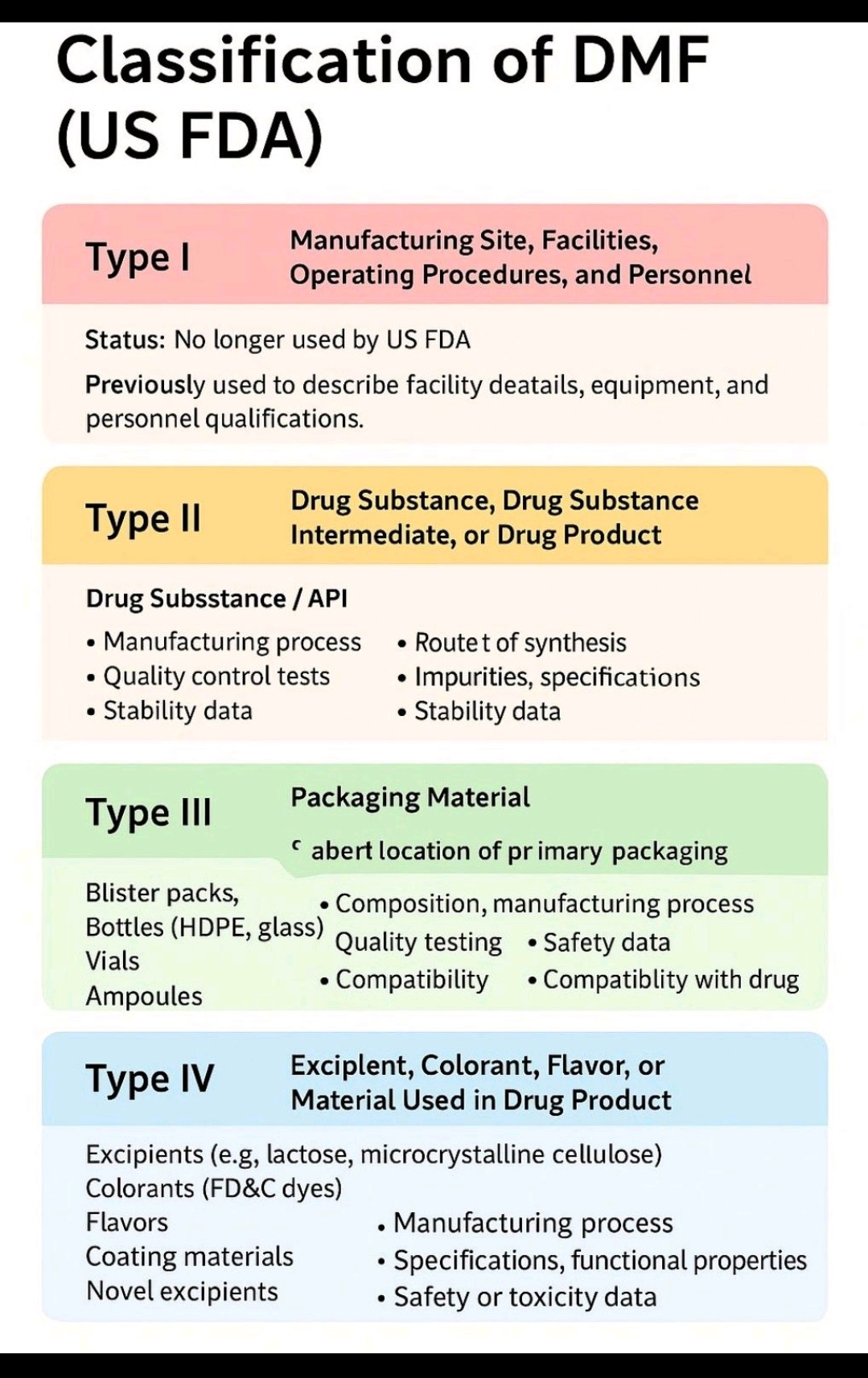
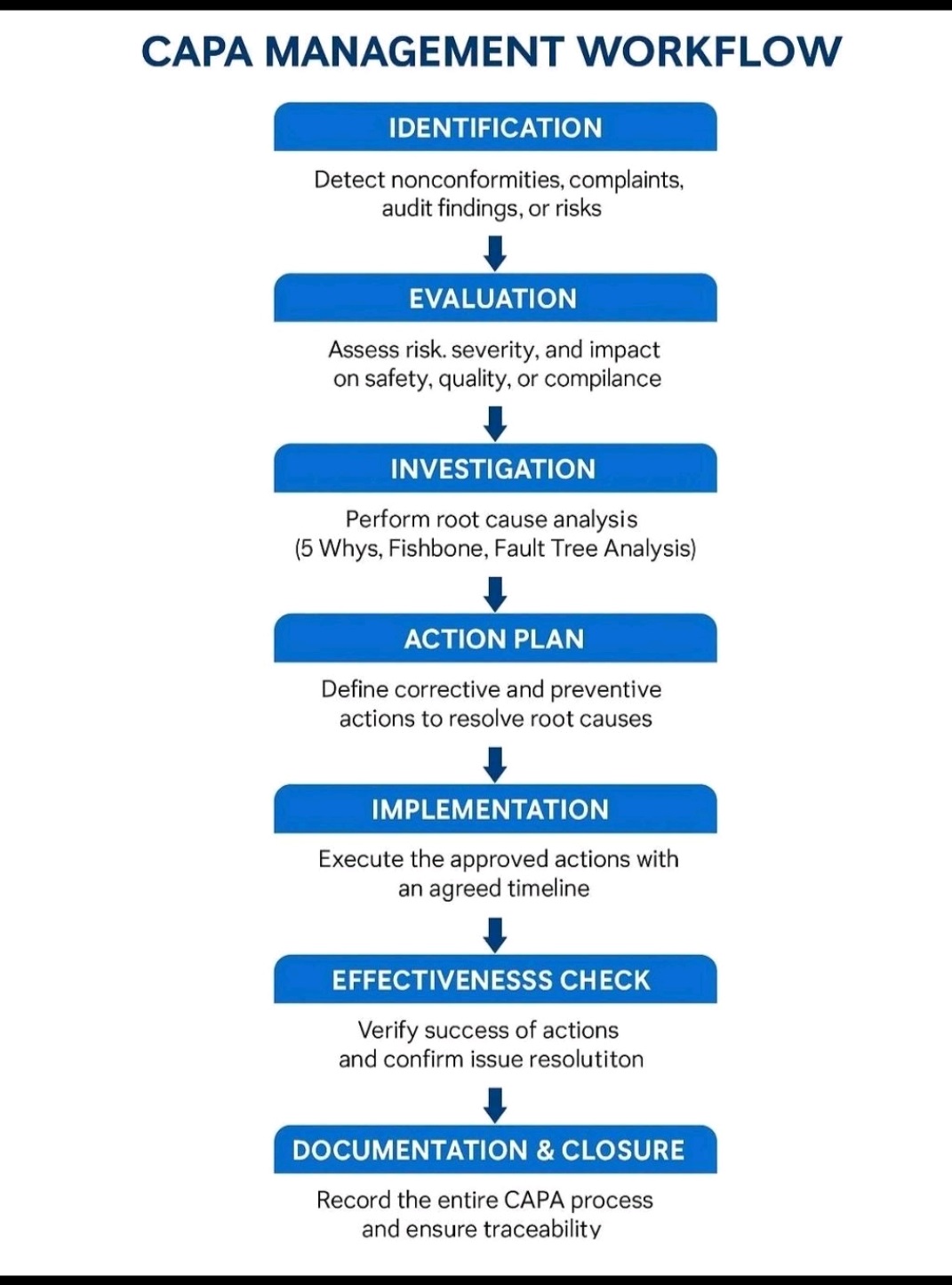
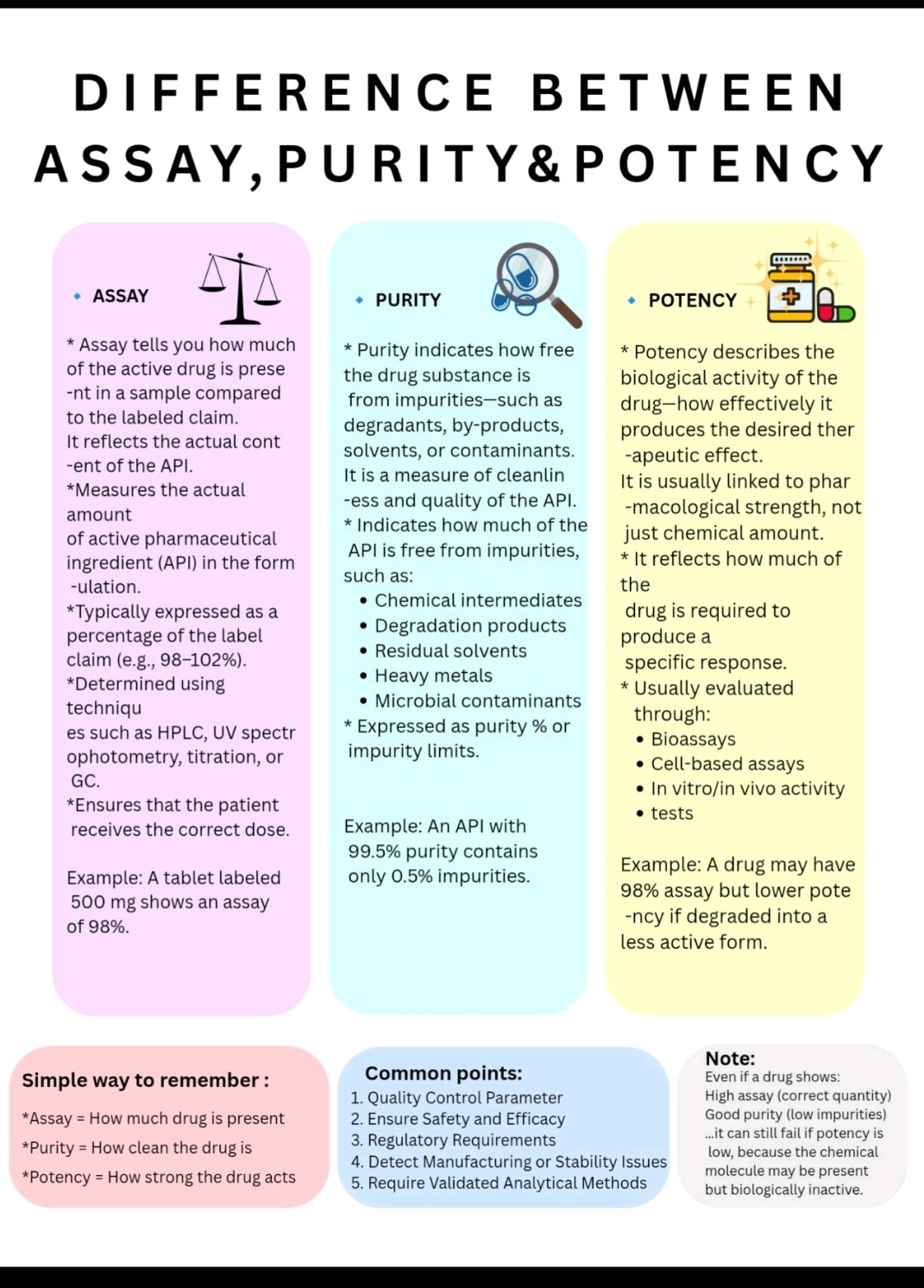
Tablet vs Capsule (Formulation)
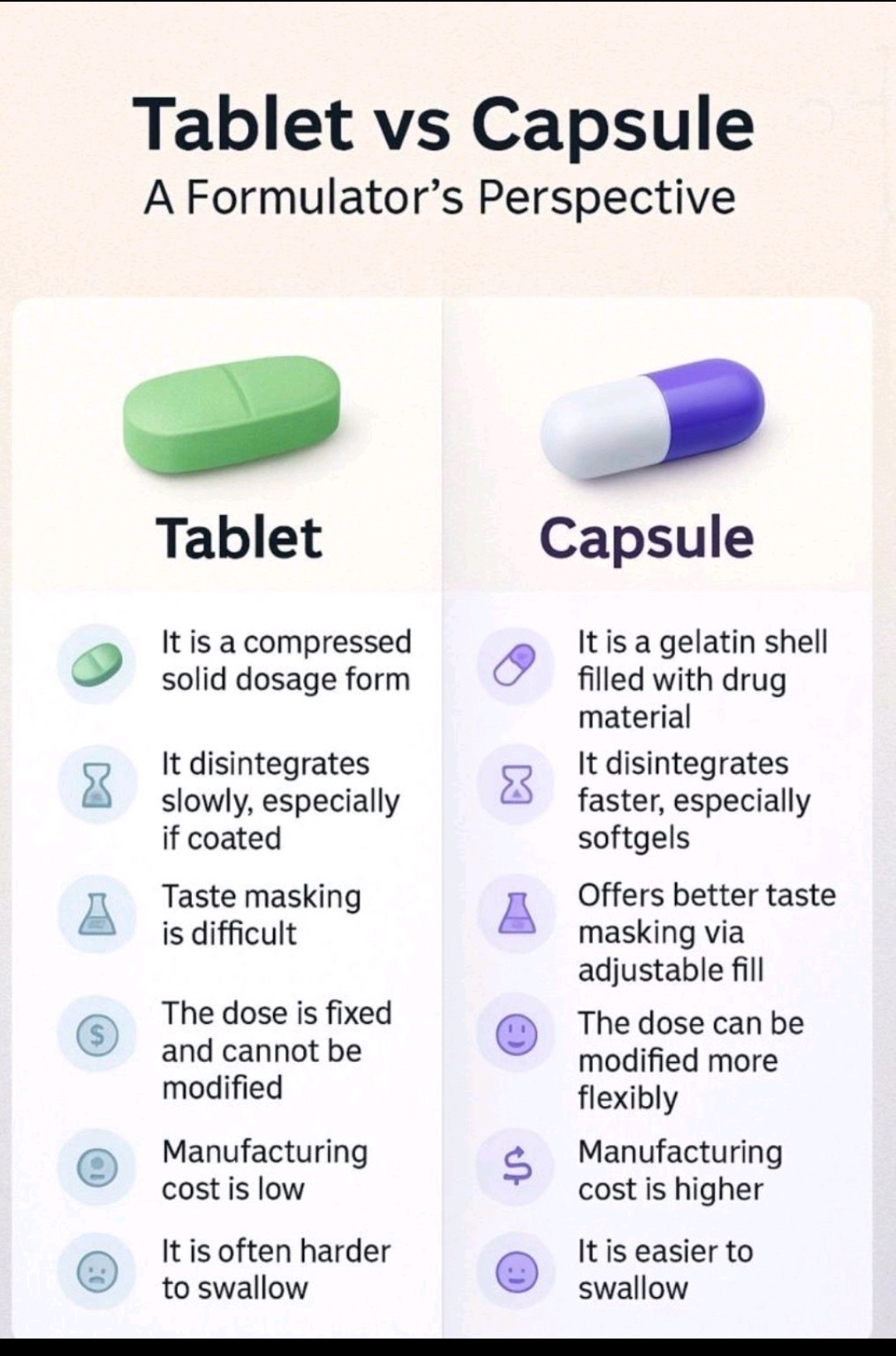
A tablet is a solid, compressed form of medication made by pressing powdered ingredients into a compact shape, which is often flat, round, or oval.
A capsule consists of medication enclosed within a soluble outer shell, typically made of gelatin or plant-based materials.